Middleware integration - CloudFront
Middleware integration for CloudFront is use to forward requests from CloudFront to wrenderer service for matching bot detection and rendering. Since wrenderer on AWS will return a JSON body containing a path key to the rendered HTML content, middleware also adjust the origin request to fetch the result from the destination path. This guide will show how to set up the middleware using Lambda@Edge functions in CloudFront.
Prerequisites
-
CloudFormation templates under
integrations/CloudFront/edgeFunctionsdirectory from GitHub repository
Setup
Following steps should all be done in
us-east-1(N. Virginia) region as Lambda@Edge only supports this region.
Step 1 - Create resources
Use CloudFormation template edgeFunctions/wrenderer-edgefunction.yaml to create Lambda functions for using in CloudFront Lambda@Edge. This will create role along with viewer request and origin request Lambda functions skeleton itself.
The
${Name}used in the steps below should be replaced with the one you choose when setting up wrenderer service.
Create CloudFormation stack
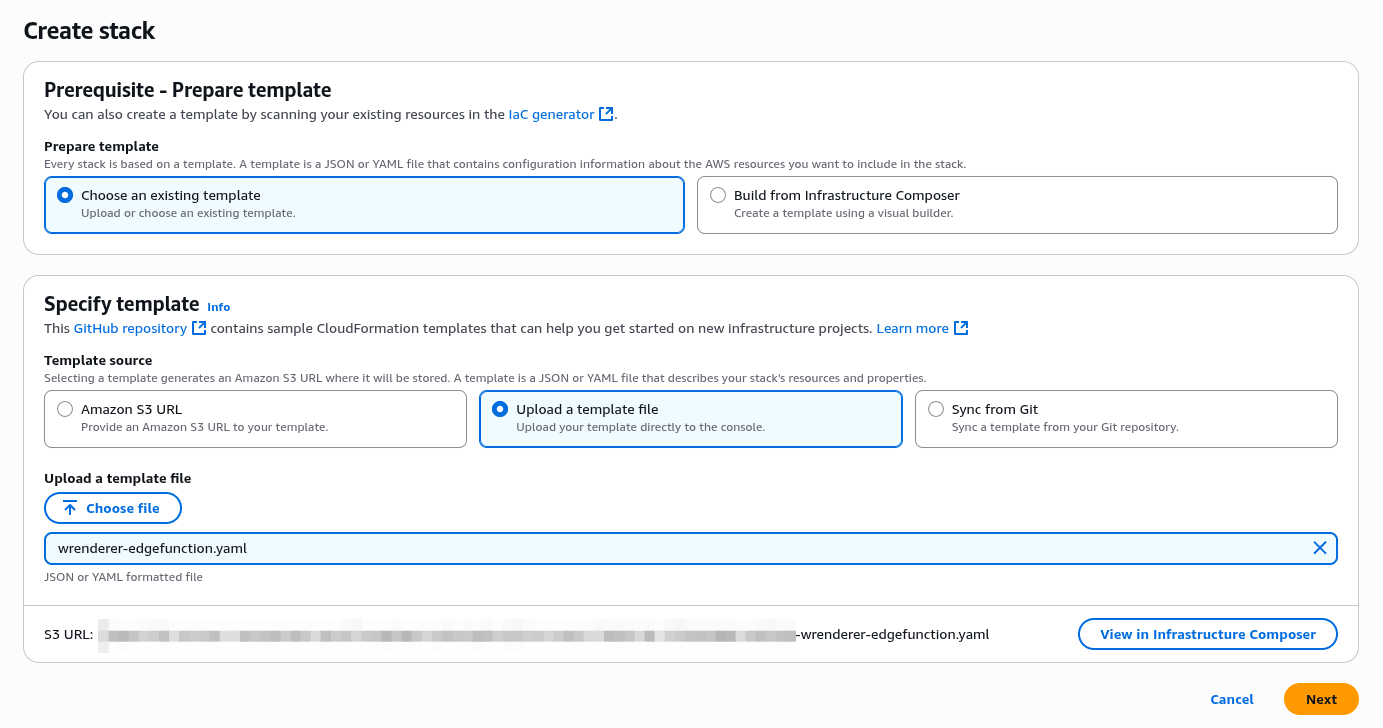
Specify stack name and parameters
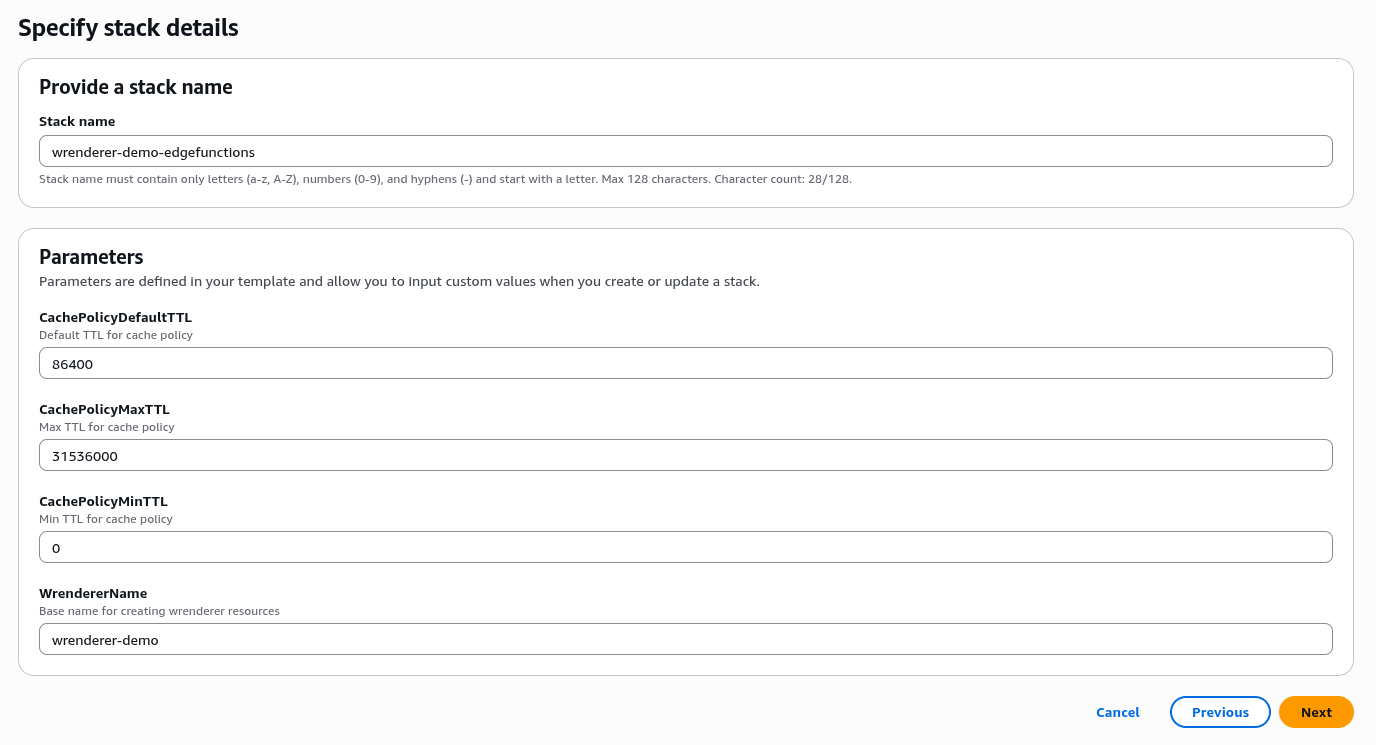
Stack name: ${Name}-edgefunctions
Parameters:
-
WrendererName:
${Name} - Other parameters can be left as default or changed as required.
Configure stack options: Keep the default options or change as required.
Review and create stack: Review the configuration and create the stack.
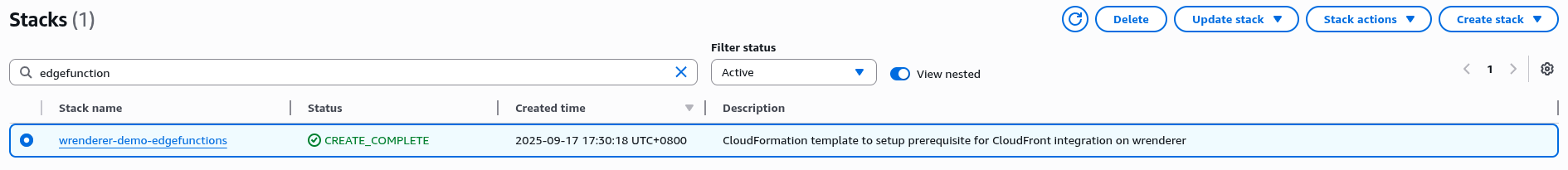
A stack with name ${Name}-edgefunctions with status CREATE_COMPLETE should be seen in CloudFormation Stacks page once creation is complete.
Step 2 - Pack and upload viewer request code
Pack code
From edgeFunctions/viewer-request directory, package the viewer-request Lambda code into a .zip archive with the command below:
# Under edgeFunctions/viewer-request directory
zip wrenderer-viewer-request.zip index.py
Upload and publish
Upload the generated wrenderer-viewer-request.zip file to the viewer request Lambda function.
-
Link to viewer request Lambda function can be found in the Resources section of the CloudFormation stack created in Step 1.
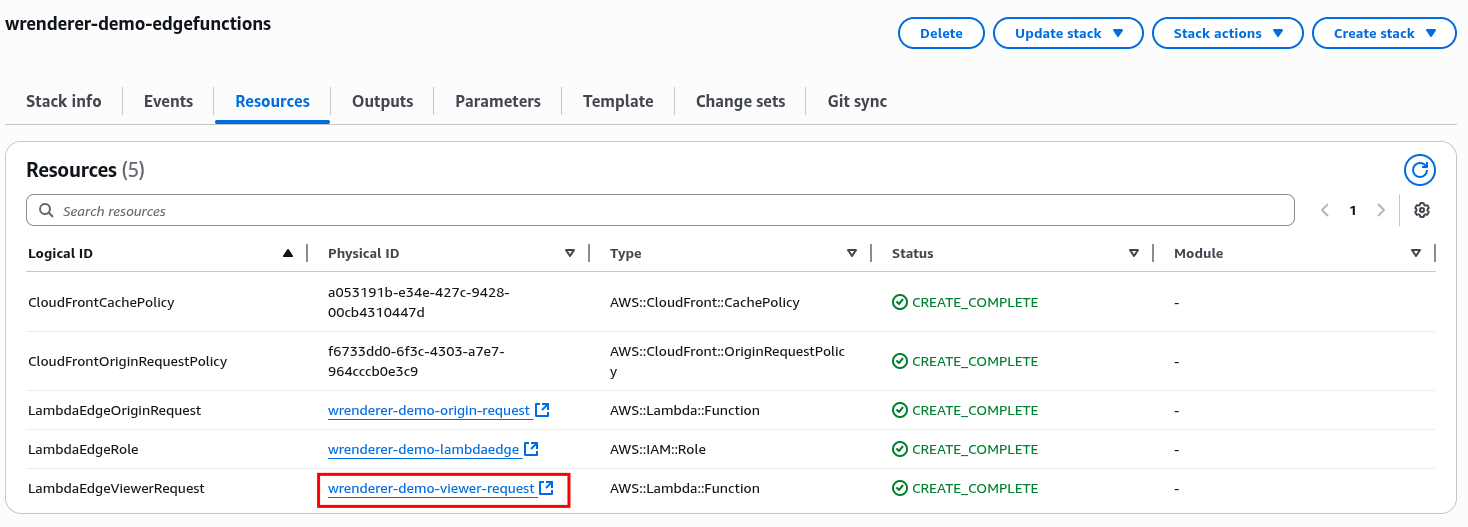
-
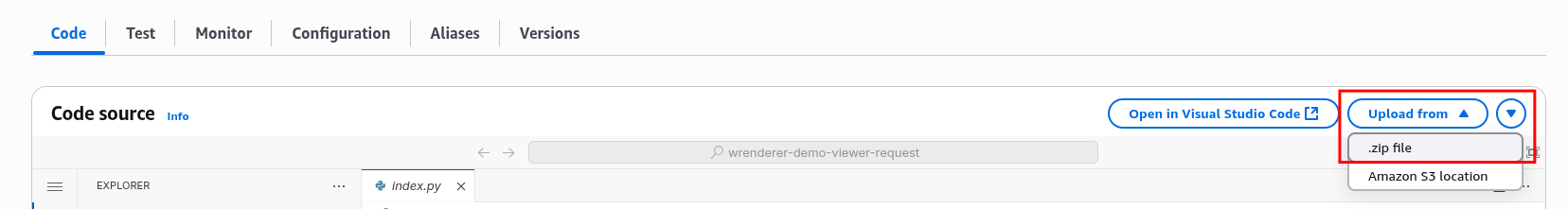
Upload the zip file into the Lambda function
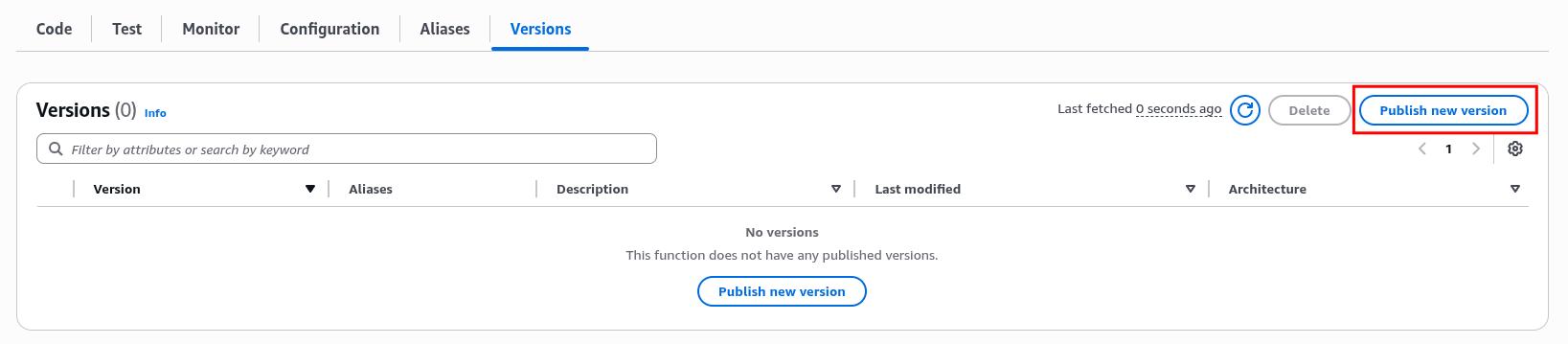
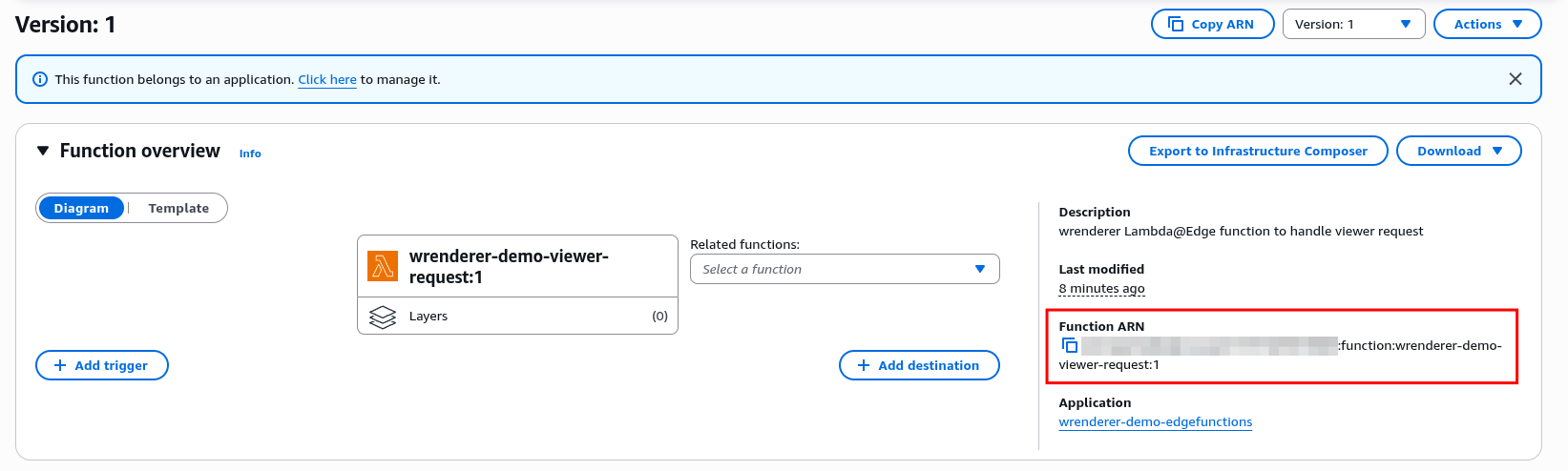
Publish a new version of the viewer-request Lambda, and record the Function ARN value shown after publishing, as it will be used in CloudFront configuration later.
Step 3 - Pack and upload origin request code
Variable setting
Fill in WRENDERER_TOKEN and WRENDERER_DOMAIN variables value in edgeFunctions/origin-request/index.py with actual value:
-
WRENDERER_TOKEN: the api key created by api gateway used for authentication in Wrenderer. See aws setup guide reference for how to find the key. -
WRENDERER_DOMAIN: the domain hosting wrenderer service. This is same as theWrendererDomainused when creating CloudFront distribution with CloudFormation template.
Pack code
From edgeFunctions/origin-request directory, package the origin-request Lambda code into a .zip archive with the command below:
# Under edgeFunctions/origin-request directory
mkdir package
pip3 install --target ./package requests
cd package && zip -r ../wrenderer-origin-request.zip . && cd ..
zip wrenderer-origin-request.zip index.py
Upload and publish
Upload the generated wrenderer-origin-request.zip file to the origin request Lambda function.
-
Link to origin request Lambda function can be found in the Resources section of the CloudFormation stack created in Step 1.
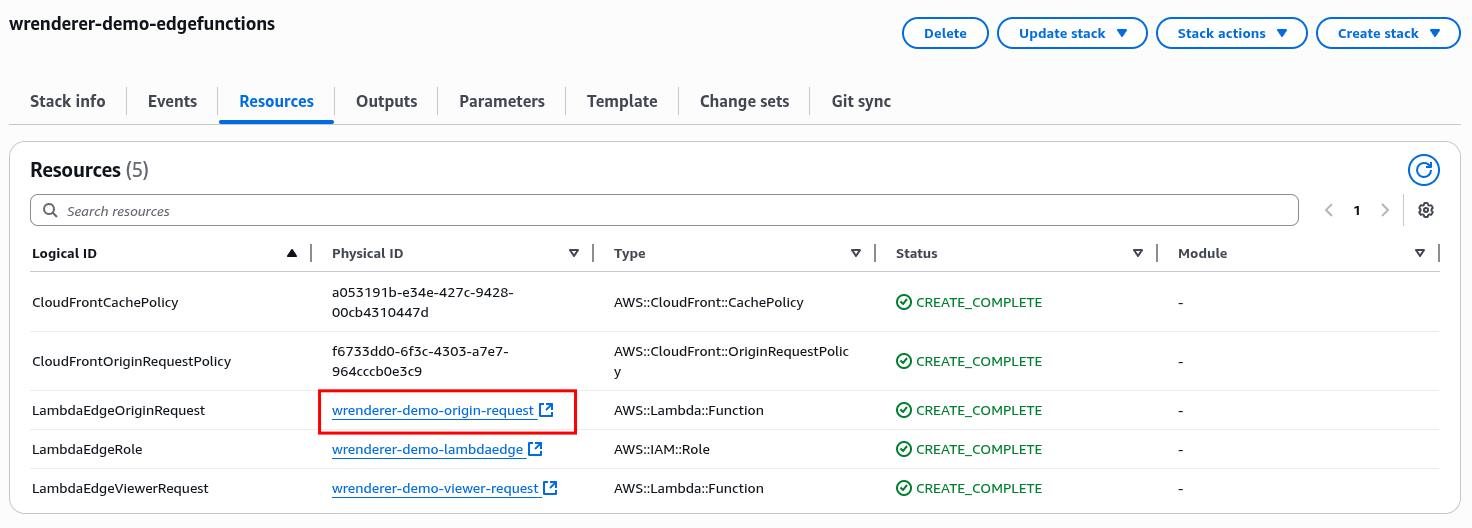
-
Upload the zip file into the Lambda function

Publish a new version of the viewer-request Lambda, and record the Function ARN value shown after publishing, as it will be used in CloudFront configuration later.


Step 4 - Configure CloudFront distribution
Configure your application CloudFront distribution to use the Lambda@Edge functions and policies created in previous steps.
Cache and origin request policy setup
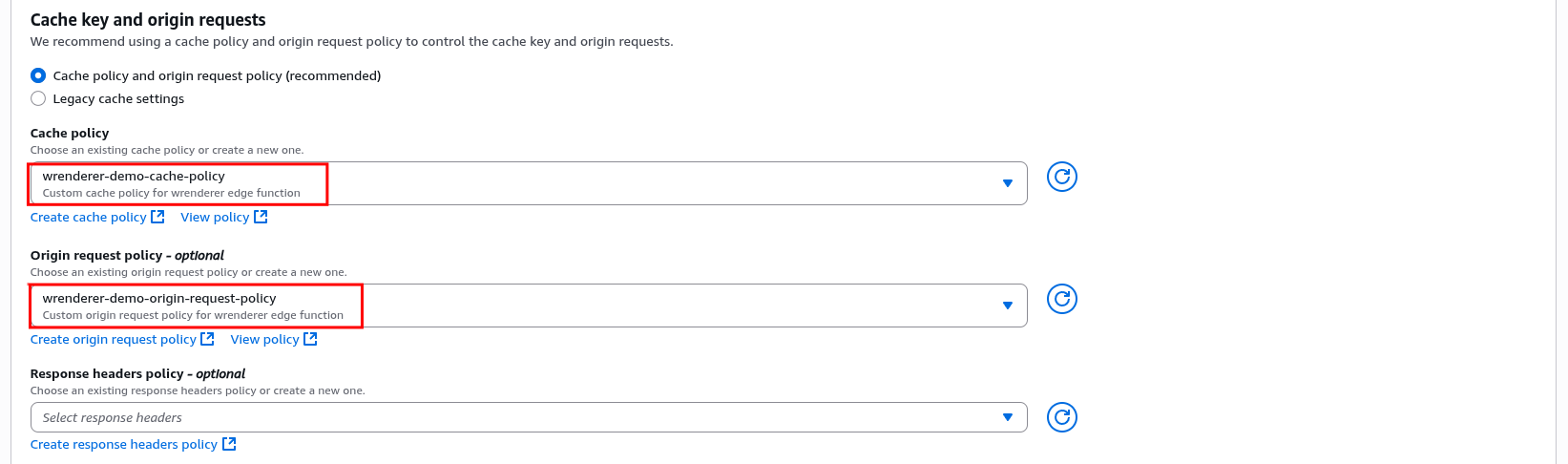
Attach the cache policy and origin request policy created by the CloudFormation template in Step 1 to the behaviors that require detection and rendering. The policies should be named as ${Name}-cache-policy and ${Name}-origin-request-policy respectively.
Lambda@Edge function setup
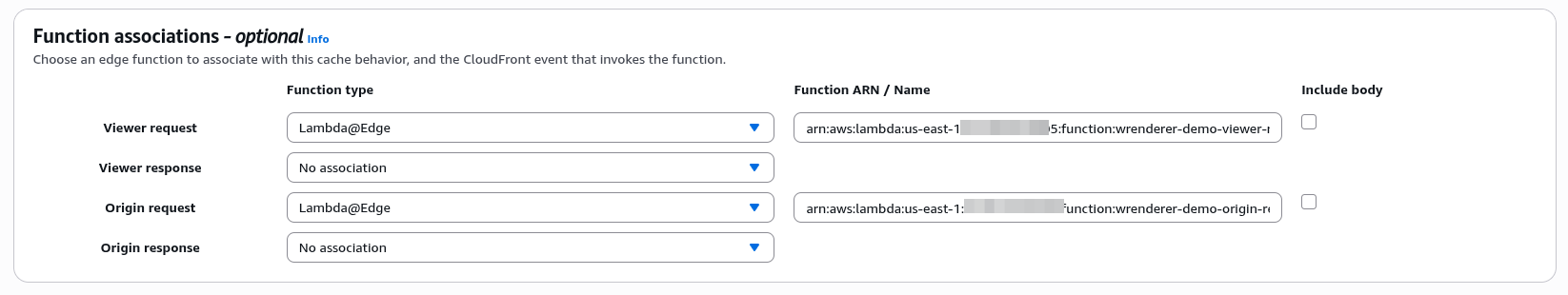
Fill in the Function ARN (versioned) of the viewer request and origin request Lambda function published in Step 2 and Step 3 respectively to the function associations of the behaviors that require detection and rendering.
Save the changes and CloudFront distribution should be ready to forward matching bots requests to the wrenderer service after the distribution is deployed.
Example
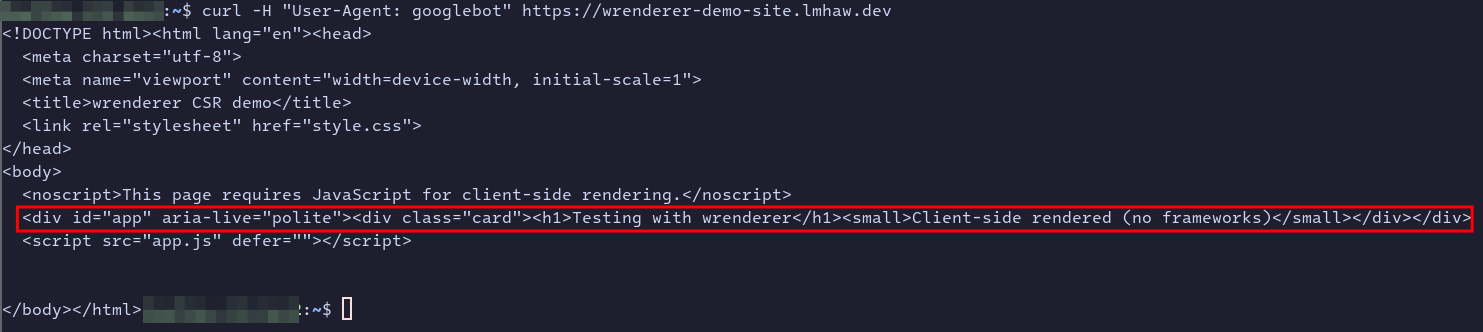
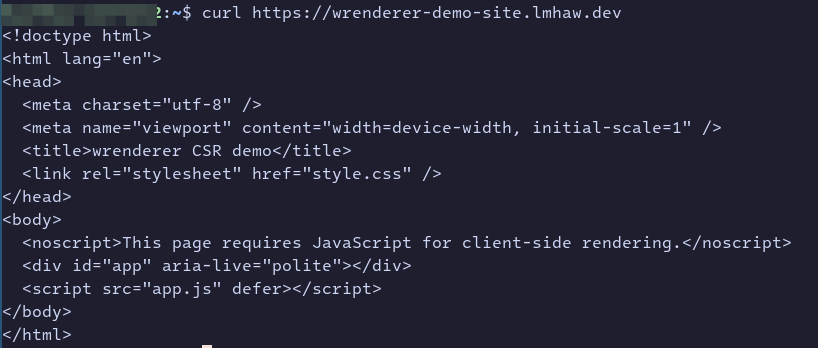
No wrenderer triggered
Trigger wrenderer with bot user-agent